I challenged myself to visualize attentions (nothing special)
nothing very special as I expected, because it was just a heat map of embeddings, next time, something better for sure. I aimed to create visualization like this research paper or by Andrej Karpathy.
I started with creating vocabulary for my model using BPE (Byte Pair algorithm). Hyperparameter for BPE merges I used is 2000-256, it would create vocab of size 2000. How? recall your learning and solve that mystery. Before running BPE on ‘Elvis Presley’ wiki page (because it was very long, no other reason), I split them into words using the Llama3 tokenizer Regex:
LLAMA3_SPLIT_PATTERN = r"""(?i:'s|'t|'re|'ve|'m|'ll|'d)|[^\r\n\p{L}\p{N}]?\p{L}+|\p{N}{1,3}| ?[^\s\p{L}\p{N}]+[\r\n]*|\s*[\r\n]+|\s+(?!\S)|\s+"""
Model. Decided to use the GPT-2 transformer architecture.
Case Study on GPT-1 and GPT-2.
GPT-1’s architecture is very similar to the original transformer presented in Attention is All You Need paper, but they use learnable positional embedding instead of Sine function. The paper proposed a framework to train language model capable of multitasking with little finetuning (as this was the trend in 2018, example ULM-FIT by Howard. Transfer learning etc). The framework consist of 2 stages, (1) learning high capacity language model on a large corpus of text, unsupervised (i.e, predict next token.) They used BPE for tokenization as it was lossless and can compress tokens. They achieved 18.4 perplexity with GPT-1 on BookCorpus dataset. (2) supervised finetuning stage, where they adapt the model for discriminative task with labeled data, like text classification, entailement, similarity, MCQ. Example would be– applying linear transformation to the output of GPT-1 model for specific task such as classification.
GPT-2 on the other hand demonstrated that the language models can perform down-stream tasks in a zero-shot setting– without any parameter or architecture modification. Highlighting the ability of language models to perform a wide range of tasks in a zero-shot setting. Small changes on the architecture of transformer is, (1) adding Normalization layer before the multihead-attention layer. (2) Adding a normalization layer before the final linear layer.
The main game changer of GPT-2 is the quality of dataset it was trained on, they created a new web scrape which emphasizes document quality. They scraped only the web pages which has been curated/filtered by humans. Manually filtering a full web scrape would be exceptionally expensive so as a starting point, scraped all outbound links from Reddit, a social media platform, which received at least 3 karma. This can be thought of as a heuristic indicator for whether other users found the link interesting, educational, or just funny.
Goal openai tried to achieve: Current systems are better characterized as narrow experts rather than competent generalists. We would like to move towards more general systems which can perform many tasks – eventually without the need to manually create and label a training dataset for each one.
ZeroShot behavior of GPT-2
Why pre-training language model is effective? Hypothesis is underlying generative model learns to perform many task in order to improve its language modeling capacity. The more structured attentional memory of the transformer assists in transfer compared to LSTMs.
How Zero shot prompts worked?
For summarization, they added text (article) and at the end TL;DR: GPT-2 Focuses on recent contents from the article or confuse specific details such as how many cars were involved in the crash or whether a logo was on a hat or shirt.
For Translation, the prompt is english sentence = french sentence
< some english sentence > = , the model the generates translated sentence, altho low accuracy because training data have only 10MB in 40GB.
Question Answering is a bit interesting and funny, figure out yourself. Go here

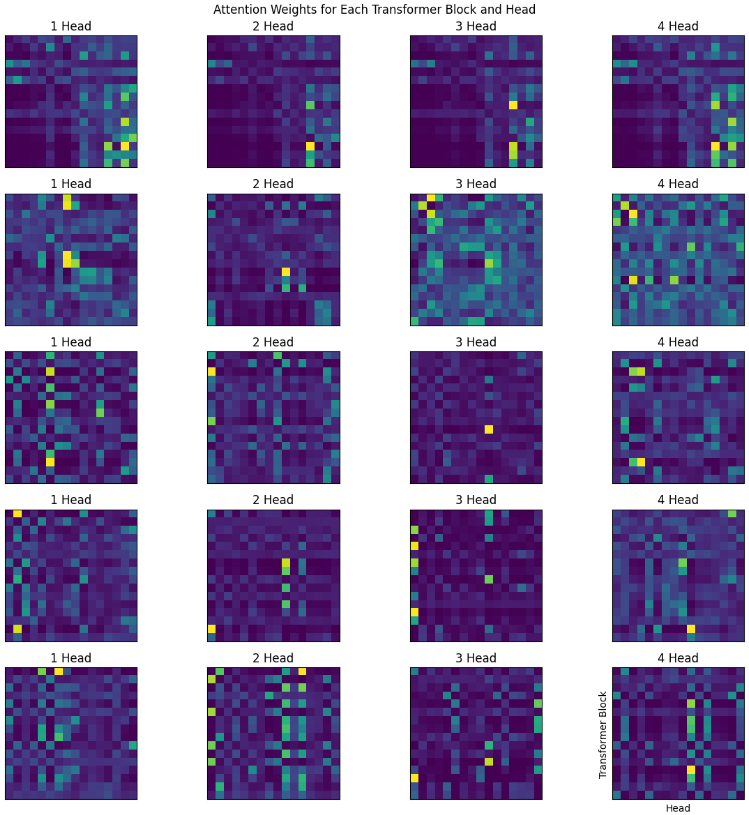
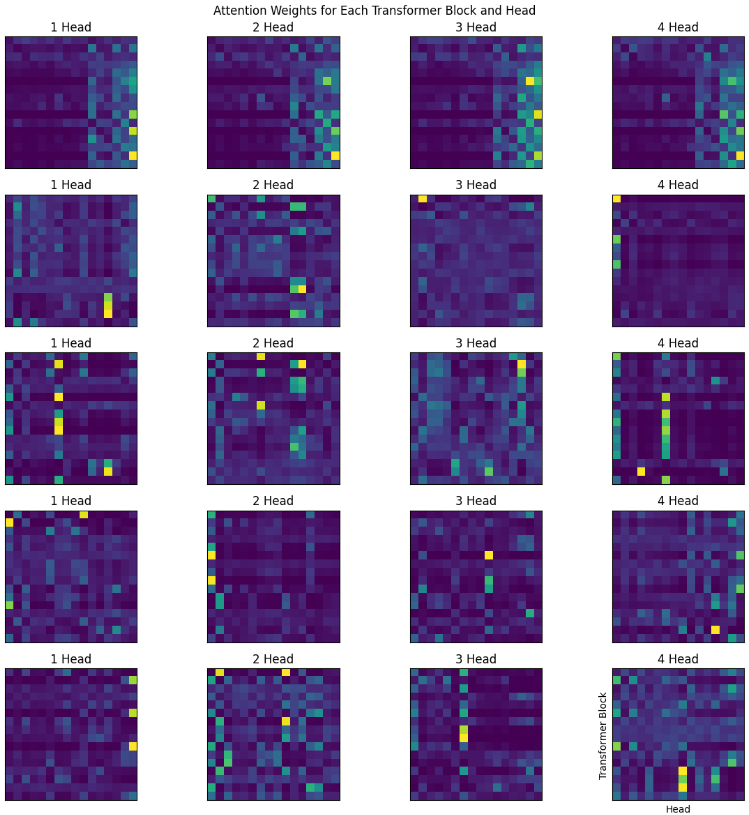
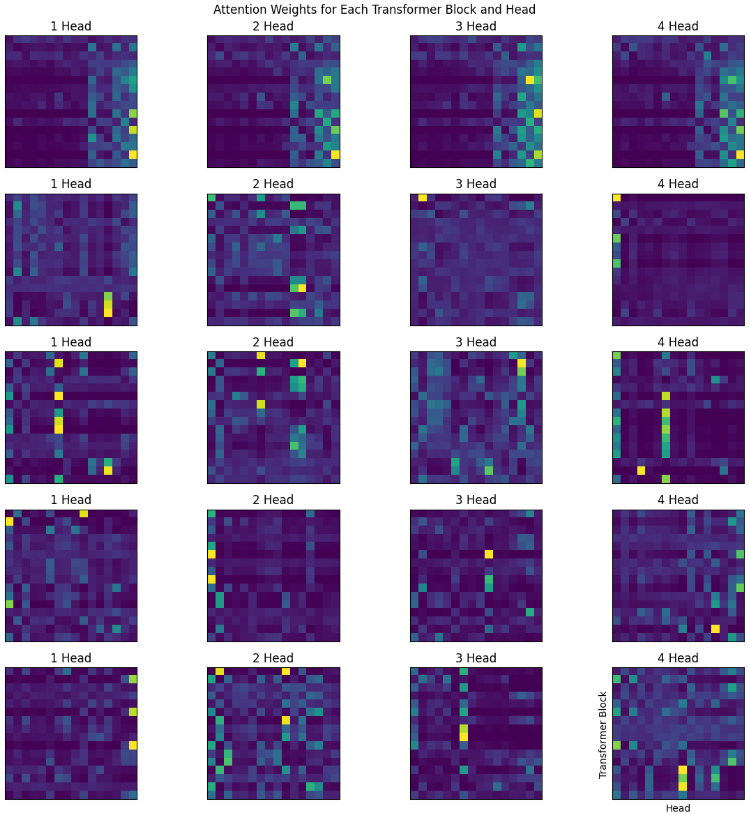
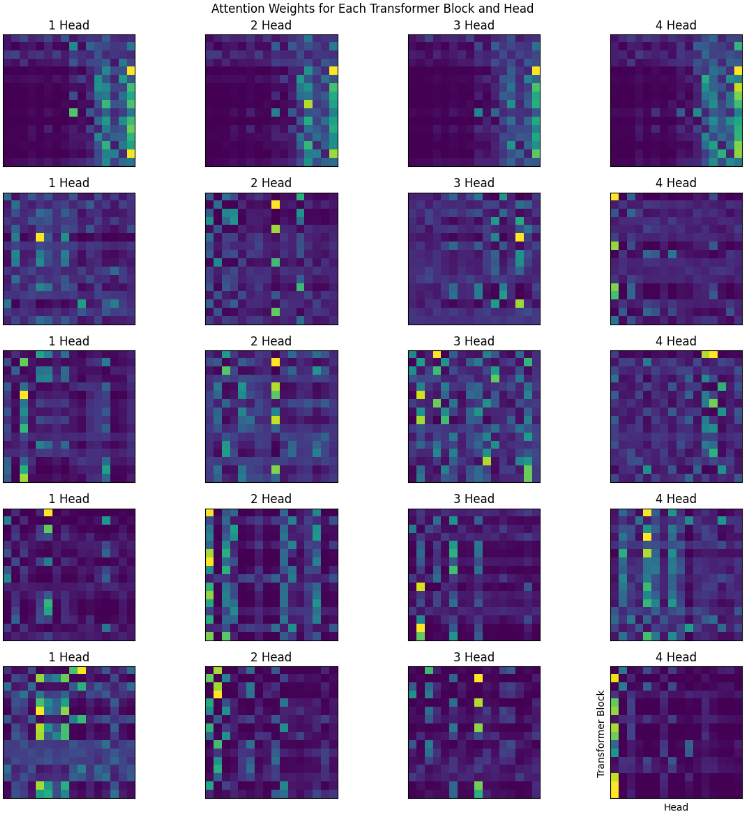
Back to visualization of attentions.
Trained the GPT-2 model, which has 4 Head, 256 head size -> 256/4 = 64 each block, 16 context size, 5 Transformer Block, 32 batch size and 64 embedding for possitional and vocab. Dropout of 0.3, and used AdamW with wd - 0.01.
Sampling code:
@torch.no_grad()
def generate(self, idx, max_new_tokens):
if type(idx) is str:
idx = torch.tensor(tkn.encode(idx), dtype=torch.long).unsqueeze(0) # add batch
for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
i = idx[:, -SL:]
logits, _ = self(i) # forward
logits = logits[:,-1,:]
probs = logits.softmax(-1)
next_idx = torch.multinomial(probs, 1)
idx = torch.cat((idx, next_idx), dim=-1)
yield next_idx
prompt = " Hello, this is"
gen = model.generate(prompt, max_new_tokens=100)
for token in gen:
token = [token.item()]
print(tkn.decode(token), end='', flush=True)
Observations.
- Gathered all the attentions from Transformer class and painted them.
- Increasing the context size (Sequence length) from 8 to 16 gave significant improvement.
- Limited with CPU, so I didn’t increase the embedding size, another reason was I also wanted to visualize them.
- Training model like GPT-2 (1.4B parameters) on a big and quality dataset, was enough to generalize diversity of Natural langauge sementics that it performed zero-shot on variety of task.
Edit: okay, I trained a small 2 layer model, with good big context length in Amazon SageMaker, here are the results.
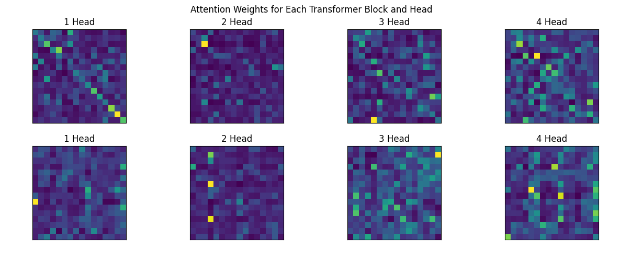
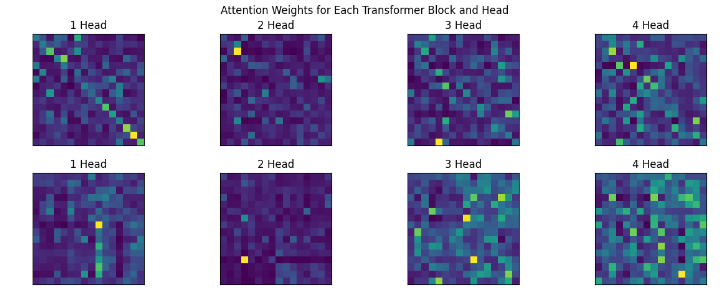
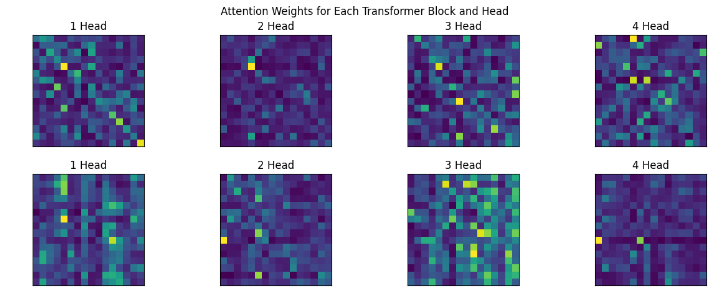
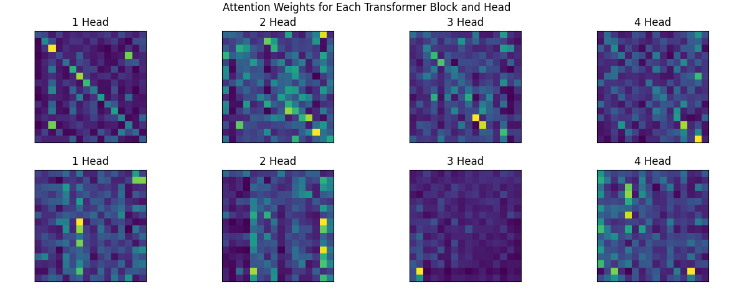
Source
- GPT-1
- GPT-2
- Visualization notebook
- Generation and Sampling notebook
- found a good read tonight, 4.4.24 edit:
- (Edit, 10th May) I found this blog, when I was reading the BERT paper which tried the similar kind of heatmaps across different layers of the transformer. Do I think like a scientist? hmm.
- (Edit, 15th May): In the Sparse Transformer paper by openai, they trained 128 layered deep network and found that attentions at different depth learns different patterns (see Figure 2.), and if you notice, (maybe) we got all the 4 above.
Outro
Reasoning in human beings refers to the cognitive process of systematically making sense of information, drawing conclusions, and solving problems through logical thinking, analysis, and inference.
What is possibility of GPT-5 or a future AI models being highly finetuned to answer with human-like reasoning? Furthermore, breaking down the training process into fine-tuning for tasks such as predicting the best possible analysis, same for logic from available information is a plausible direction for advancement. Just a thought.